Cardboard core
Although cardboard cores (also knowed as cardboard tubes) are simple and cheap, they’re a basic raw material for making a wide range of products. Cardboard cores are used, for example, in the final phases of texile material reel packaging, adhesive tapes, yarns and printed labels on paper or plastic films.
Cardboard cores for paper and label factory are made through the wrapping of recycled cardboard and they’re designed to hold very heavy loads.
In print houses and label factories cardboard tubes are employed in the final step of the manufactoring process, when the printed and die cut paper reels are wrapped by the control table on resistant cardboard pipes.
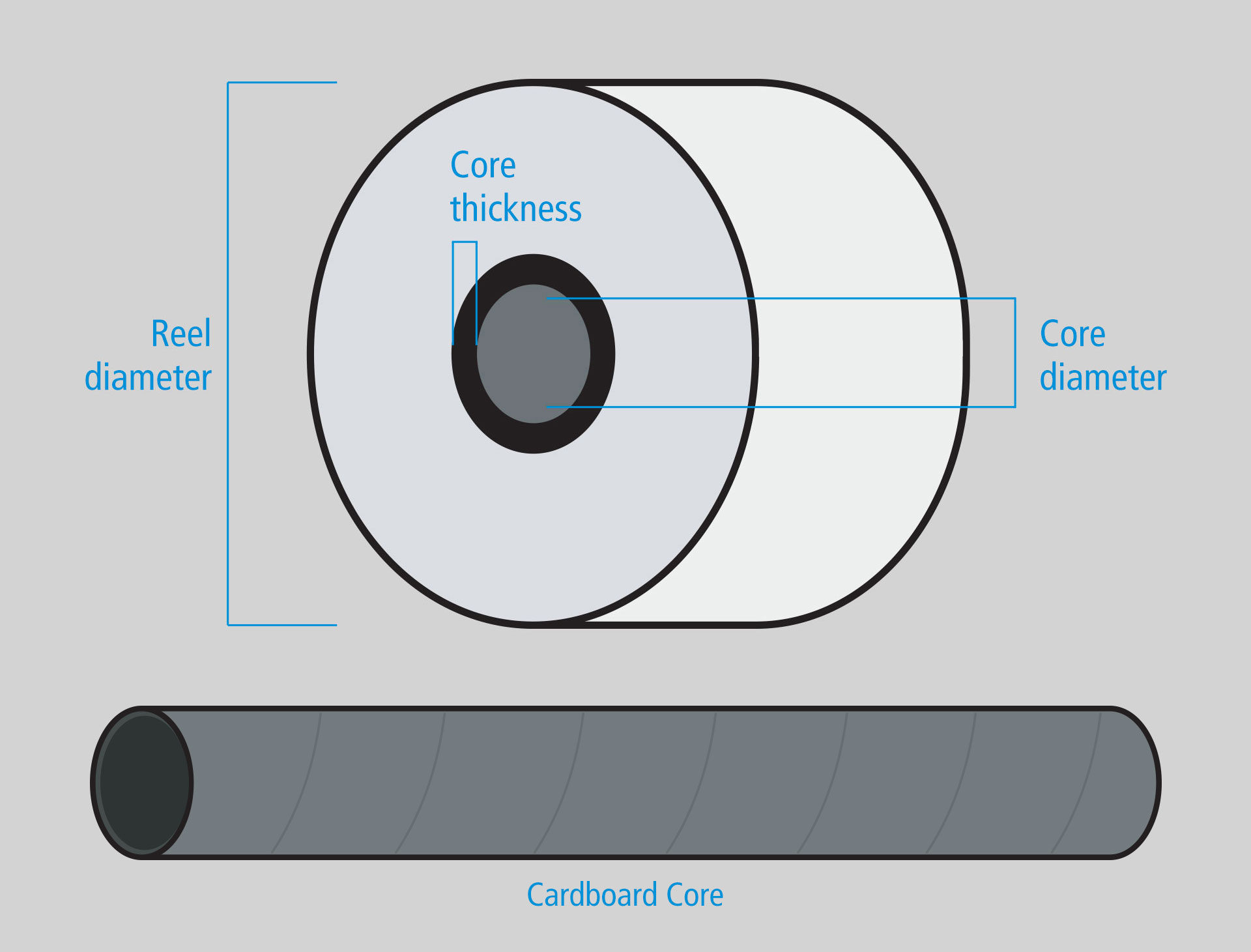
Cores could have different internal diameters and thickness.
Customers who buy labels from printing houses usually suggests which kind of core they want the final product to be wrapped with, according to their assembly needs or to their labelling machines ones.
The most requested internal diameters of the cardboard tubes usually are 38 mm, 45 mm and 75 mm. Thickness range coupled with these diameters goes from 3 mm to 8 mm.
Obviously thickness determines the endurance of the cardboard core. Higher is this value more the tube could resiste to compression. To endure bending in the most efficient way, bigger internal diameters are coupled with thicker cores.
Thicker cores could be requested, not only coupled with bigger internal diameters, but also when the tube length is higher, to retain the straightness of the product.
Label industries buys already cut to measure cardboard cores, or jumbo formats (from 1000 mm length on) from which they could obtain the cut they need.
This page is part of Gerp's glossary of terms. Gerp is a dedicated MIS to packaging industry. You are welcome to browse this website or contact us for more information.